The Social Security Payroll Tax Can Best Be Described as a
Payroll taxes fund social insurance programs including Social Security and Medicare and are the second-largest source of revenues for the federal government. In 2019, the most recent year for which data were not afflicted by temporary distortions resulting from the pandemic, payroll taxes made up 36 percent of total federal revenues. Most working Americans are subject to payroll taxes, which are usually deducted automatically from an employee'due south paycheck. Employers are too frequently field of study to those types of taxes.
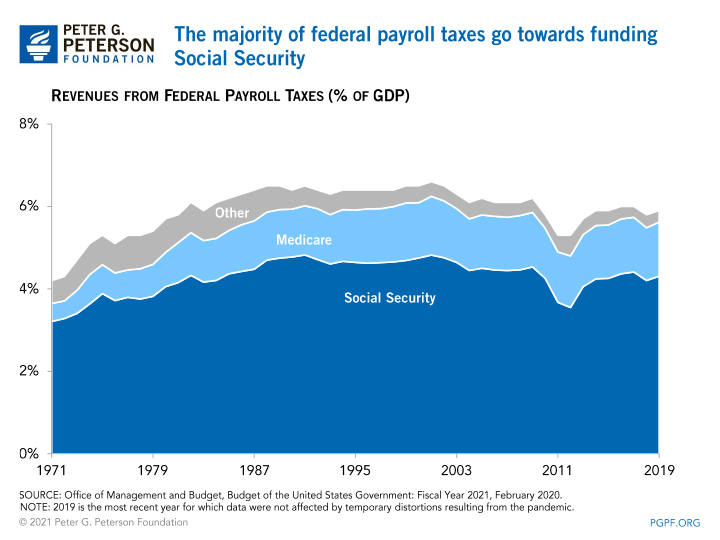
The vast majority of federal payroll taxes get towards funding Social Security and Medicare:
- Taxes directed to the Social Security program were created past the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) and are levied equally on employers and employees on all wages upwards to a certain level.
- Medicare taxes for its Hospital Insurance (HI) program are likewise role of FICA and are levied as on employers and employees on all wages. The Hi trust fund besides receives inflows from a supplemental tax on high earners.
A few other types of federal payroll taxes besides fund smaller programs:
- Employers pay taxes to fund the Unemployment Insurance program.
- Programs to fund retirement for federal employees and railroad workers as well receive revenue from payroll taxes.
TWEET THIS
What Is the Social Security Payroll Tax?
The portion of FICA taxes that is dedicated to Social Security is used to fund the Old-Age and Survivors Insurance and Disability Insurance programs, which provide income on a monthly ground to retirees, people with disabilities, and their families. Payroll taxes are the primary source of funding for those programs, bookkeeping for 88 pct of all inflows into their trust funds in 2019.
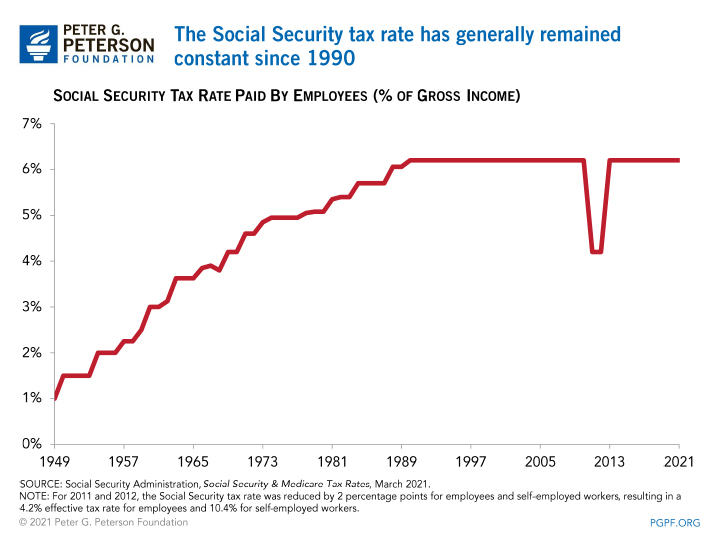
Employers and employees each pay 7.65 percent of payroll in FICA taxes; the portion dedicated to Social Security is 6.2 percent and is only levied up to a maximum income level adamant annually (the remaining ane.45 percentage is designated for Medicare). Self-employed individuals also contribute to these funds through Self-Employment Contributions Act (SECA) taxes. The rates for SECA taxes are identical to those for FICA taxes, with the only difference beingness that the individual is responsible for paying both employee and employer portions of the tax.
The tax rate for Social Security was originally ready in 1937 at 1 percent of taxable earnings and increased gradually over time. The current rate was set up in 1990, although information technology has been modified twice in response to economic downturns. In 2022 and 2012, the rate for employees was temporarily lowered to aid alleviate the hardship resulting from the Great Recession. To increase take-home pay during COVID-nineteen, employers were allowed to defer withholding some of their employees' share of payroll taxes for Social Security from September i, 2022 through December 31, 2020. However, employers are responsible for withholding any deferred taxes from employee wages and paying them by the end of 2021.
TWEET THIS
In 2019, Social Security received $914 billion in acquirement from payroll taxes, or four.iii per centum of gross domestic product (GDP). The remainder of the program's inflows come from taxation on Social Security benefits too as interest on the balances of the trust funds.
What Is the Limit on Earnings Subject field to the Social Security Payroll Tax?
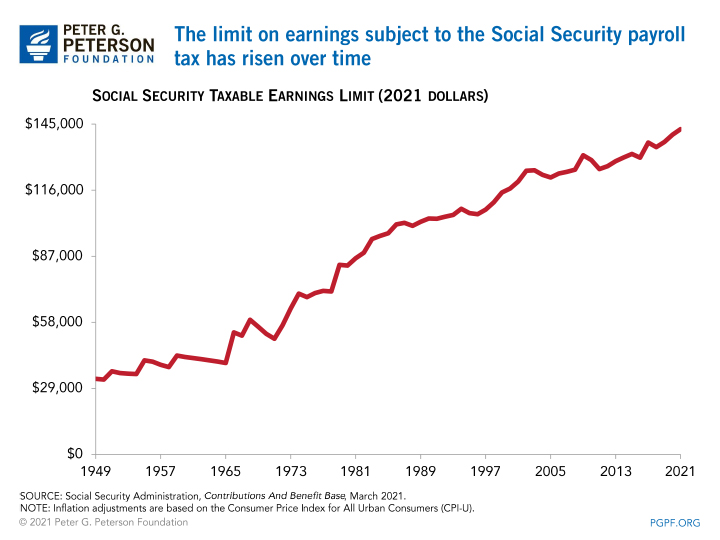
The Social Security payroll tax merely applies up to a certain amount of a worker'south annual earnings; that limit is often referred to equally the taxable maximum or the Social Security tax cap. For 2021, the maximum earnings subject to the Social Security payroll tax is set at $142,800, an increase of $five,100 from the 2022 level.
When the tax dedicated to Social Security was kickoff implemented in 1937, it was capped past statute at the kickoff $3,000 of earnings (which would exist equivalent to about $56,000 in 2022 dollars). Since 1975, the taxable maximum has generally been increased each year based on an index of national average wages. Each year, nearly 6 percentage of the working population earns more than the taxable maximum, which has been the case since 1983.
TWEET THIS
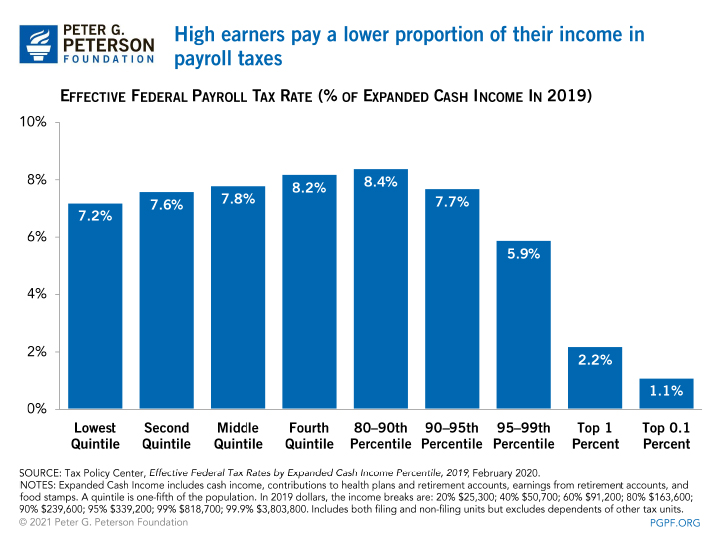
Economists consider the Social Security tax to be regressive, because as an private's earnings increase above the cap, the portion of total earnings that is taxed decreases.
TWEET THIS
Arguments For and Against the Social Security Tax Cap
Proponents of increasing or eliminating the limit on earnings field of study to the Social Security payroll tax fence that it would make the taxation less regressive and exist office of a solution to strengthen the Social Security trust funds. An analysis from the Congressional Budget Part estimated that phasing out the taxation cap past subjecting earnings below the current taxable maximum and above $250,000, would have raised over $i trillion in revenues from 2022 through 2028. Some other argument is that removing the taxable maximum would adjust for the fact that higher-income individuals generally have longer life expectancies and thus receive Social Security benefits for a greater amount of time.
Opponents fence that increasing or removing the taxable maximum would weaken the link between the amount individuals pay in Social Security taxes and the amount they receive in retirement benefits. Opponents besides contend that while depression-income earners may pay a greater share of their income in Social Security taxes than those who are wealthier, they likewise receive a asymmetric share of government transfer payments that are non bailiwick to the tax. Those opponents cite programs that have been created to — at least partially — get-go the regressive nature of the Social Security payroll tax.
Some economists anticipate that if the limit were lifted, employers might reply by shifting taxable compensation to a form of compensation that is taxed at a lower rate. For example, employers could decrease wages but increment retirement benefits, which are deductible nether the corporate income revenue enhancement, in an attempt to starting time the boosted payroll taxes they would owe.
What Is the Medicare Payroll Tax?
Employees and employers each contribute 1.45 percent of earnings by workers to Medicare, which is levied on all income. Since 2013, an additional 0.9 percent tax has been imposed on employees with earnings exceeding a threshold betwixt $125,000 and $250,000 depending on filing status; those additional taxes are not matched by the employer.
The revenue from payroll taxes help fund Medicare's Infirmary Insurance (Hullo) plan, which is used to pay for hospital stays and a few forms of home healthcare, such as hospice care. For 2019, HI tax revenues were 1.iii percent of GDP, an amount that has been relatively constant for 25 years. The HI tax was originally the primary source of revenues for Medicare before the program grew to include Medicare Advantage plans and prescription drug coverage. The taxes dedicated to HI now make up 36 pct of Medicare'southward total inflows, a share that is projected to decrease going forward.
Are At that place Other Federal Payroll Taxes?
In addition to FICA or SECA taxes, a few other payroll taxes are levied on certain employees:
- Federal Unemployment Revenue enhancement Deed (FUTA) taxes are but paid past employers, at a rate of six pct for the first $7,000 of earned income per employee. FUTA taxes support funding for state-administered unemployment insurance programs.
- Railroad Retirement Human action taxes are paid by railroad employees and employers to fund retirement programs for railroad workers.
- Other payroll taxes are mostly comprised of taxes paid past federal employees to fund their own retirement programs.
How Do Payroll Taxes Work in Other Countries?
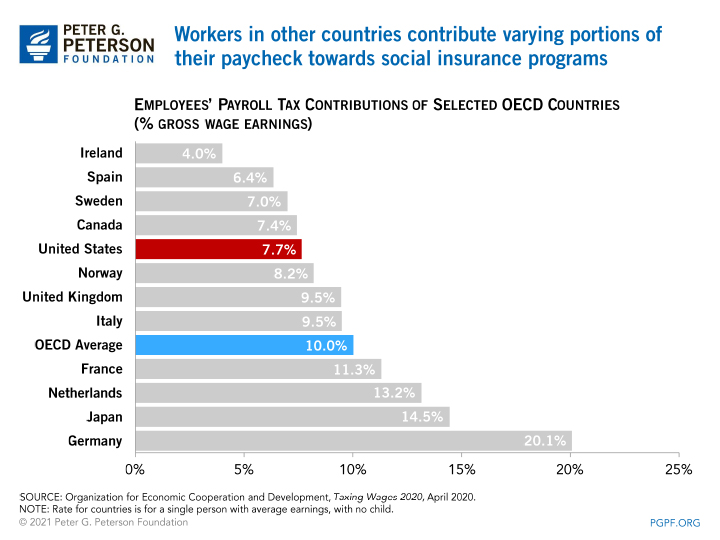
Many countries in the Arrangement for Economical Co-operation and Development (OECD), a group of nations with high-income economies, also fund their social insurance programs with payroll taxes. While the Social Security systems of other countries take different forms, most provide authorities-financed pensions that provide income assistance for retirees, similar to that of the United states.
Despite that similarity, in that location is much variation in how other OECD countries impose payroll taxes on their citizens. Countries such as holland, Sweden, Germany, and Canada accept caps on taxable earnings that are lower than in the United States; others, such as Norway and Ireland, tax all earnings. Generally, countries with higher payroll tax rates have lower caps, while countries with lower payroll tax rates, like the United States, tend to take higher caps or no caps at all. In some OECD countries, social insurance programs are funded through other sources such as income taxes or excise taxes.
Certain countries, similar the United Kingdom and Austria, have a bracketed payroll tax structure that levies the payroll tax at different rates depending on total income, similar to how the U.s. levies income taxes. In the Uk, that bracketed system is regressive in structure, while in Austria it is progressive.
TWEET THIS
Conclusion
Payroll taxes are an important component of America'south system of tax and they fill an essential role in keeping social insurance programs funded and operational. Payroll taxes represent the second-largest source of federal revenues, subsequently income taxes. On the household level, payroll taxes are oft the primary federal tax an individual will incur; in fact, nigh two-thirds of households pay more in payroll taxes than income taxes, according to the Taxation Policy Heart.
Social insurance programs, primarily Social Security and Medicare, face serious fiscal challenges. Those challenges will probable accelerate due to the decline in economic action and payroll tax revenues caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and legislation in response to it. Agreement how programs are funded through payroll taxes is important for developing reforms that volition ensure that those programs can proceed to provide benefits to the recipients who depend on them.
Source: https://www.pgpf.org/budget-basics/budget-explainer-payroll-taxes
0 Response to "The Social Security Payroll Tax Can Best Be Described as a"
Post a Comment